|
Structured Investment Products (SIP) are investment
products structured to meet investor's individual risk-return criteria.
Returns may not be necessarily in line with the performance of the
underlying assets. The aim is to exceed these performance levels on
a risk adjusted basis.
SIP is normally a composite of bond, asset, and derivative instruments. For further information on SIP trading on the iMarkets' platform, please contact iMarkets Partner Firms.
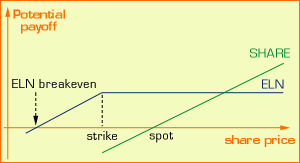
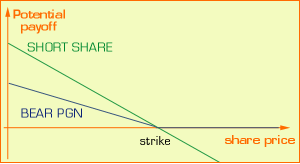
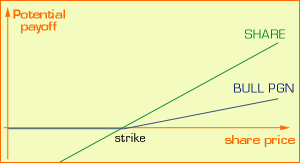
Examples of SIP
|
![]()
This website is intended to be accessed by sophisticated and professional investors in Hong Kong only.
The information on this site were made available solely for information purposes and do not constitute an offer, solicitation or recommendation with respect to buy or sell any investment products, or securities, or financial products and instruments (the "Products"), or to participate in any particular trading activities or strategies. Analysis and information have not been independently verified, and any trade executed on the basis of these information are taken at the investors' own risks. Investors are advised to have sufficient knowledge and experience in financial and business matters to evaluate the merits and risks of investing in any of these Products, and should be able to bear the risks of an investment.
The information on this site were obtained from sources believe to be reliable. iMarkets Ltd. makes no express or implied representations or warranties concerning the completeness or accuracy or otherwise of these information and accept no responsibility or liability whatsoever for any loss or damage arising from these information.
The price and income of anyof the Products referenced in this site may experience upward or downward movements, and may even become valueless. There is an inherent risk that losses may be incurred rather than profit made as a result of buying and selling these Products. Past performance is not necessarily indicative of future performance.
The risk of loss in trading futures contracts or options can be substantial. In some circumstances, you may sustain losses in excess of your initial margin funds. Placing contingent orders, such as "stop-loss" or "stop-limit" orders, will not necessarily achieve the desired results. Market conditions may make it impossible to execute such orders. You may be called upon at short notice to deposit additional margin funds. If the required funds are not provided within the prescribed time, your position may be liquidated. You will remain liable for any resulting deficit in your account. You should therefore study and understand futures contracts and options before you trade and carefully consider whether such trading is suitable in the light of your own financial position and investment objectives.